Stem Cell Transplant: A Promising Treatment for Various Diseases
Understanding the Potential and Application of Stem Cell Transplantation
Introduction:
Stem cell transplant, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation or bone marrow transplant, is an innovative medical procedure that harnesses the regenerative power of stem cells to treat a variety of diseases. This cutting-edge approach offers hope to patients with conditions that were previously considered incurable. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of stem cell transplantation, its remarkable benefits, and the range of diseases it can effectively address.
 What is Stem Cell Transplantation?
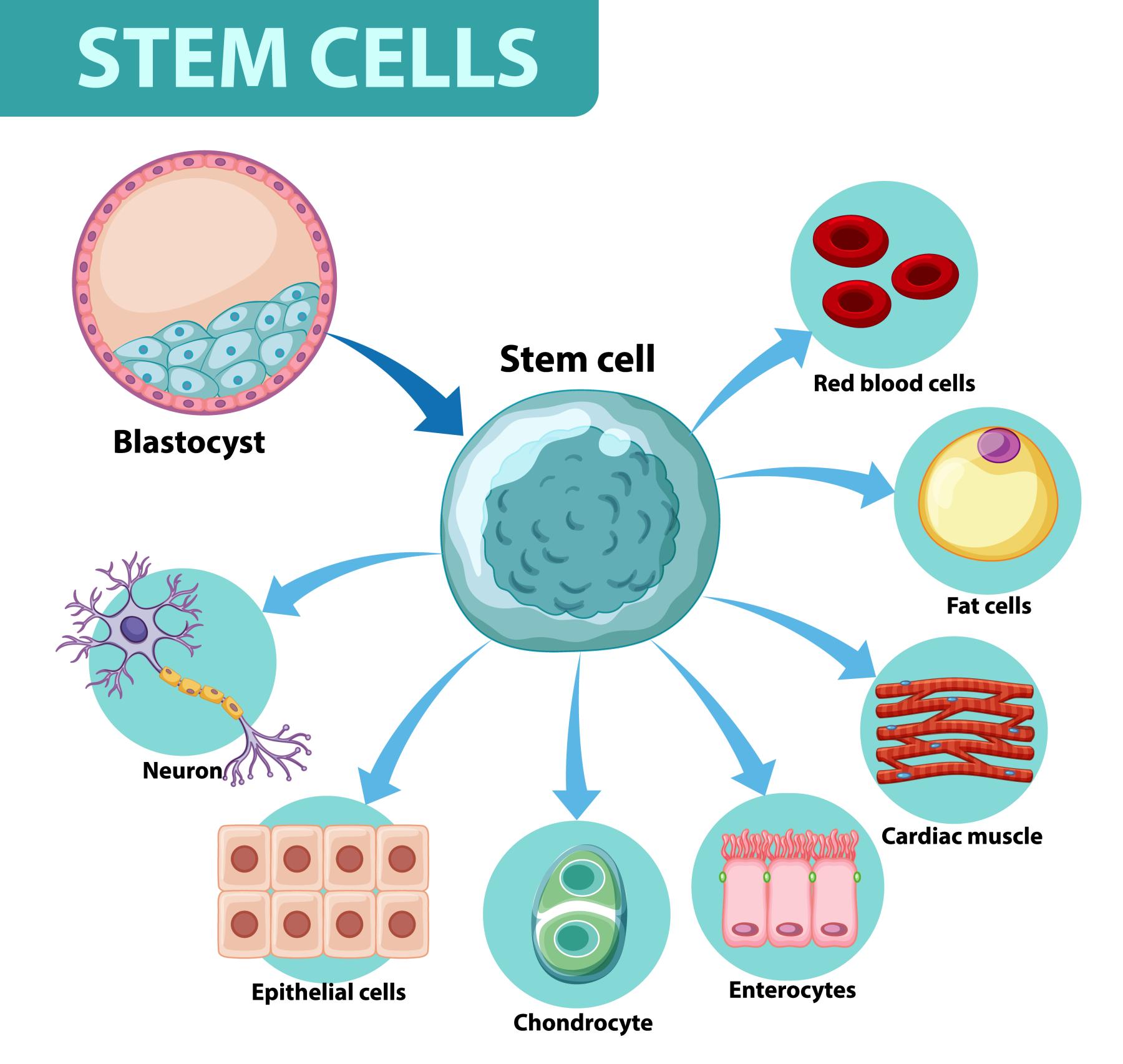
What is Stem Cell Transplantation?
Stem cell transplantation involves the infusion of healthy stem cells into the body to replace damaged or dysfunctional cells. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into specialized cell types. They can be derived from various sources, such as bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood.
The Benefits of Stem Cell Transplantation:
Stem cell transplantation holds immense promise due to its regenerative potential and versatility. By replacing damaged cells with healthy ones, it can restore the body's ability to produce essential blood cells, repair damaged tissues, and rejuvenate the immune system. Moreover, stem cells have the remarkable ability to migrate to sites of injury, aiding in tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation.
Conditions Treated with Stem Cell Transplantation:
Hematological Disorders: Stem cell transplantation is commonly used to treat a wide range of hematological disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and aplastic anemia. It allows for the replacement of cancerous or diseased cells with healthy ones, offering a chance for remission or cure.
Immune System Disorders: Stem cell transplant can be a viable option for individuals with severe immune system disorders such as severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, or certain primary immunodeficiency diseases. By replenishing the immune system with healthy cells, it enhances the body's ability to defend against infections and diseases.
Genetic Disorders: Some genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, and certain metabolic disorders, can be treated with stem cell transplantation. By introducing healthy stem cells into the patient's body, the defective cells responsible for the disorder can be replaced, potentially offering a long-term solution.
Solid Organ Cancers: Stem cell transplantation is also being explored as a potential treatment for solid organ cancers, including breast, lung, and ovarian cancer. The aim is to replace cancerous cells with healthy stem cells, thereby regenerating healthy tissue and aiding in the recovery process.
What is the success rate of Stem Cell Transplant?
The success rate of stem cell transplant varies depending on the specific condition being treated. Generally, for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in certain diseases like leukemia, the success rate can range from 80% to 90%, while for other conditions, the success rate may be lower or higher. Factors such as the patient's overall health, disease stage, and the source of stem cells used can influence the outcome.
What is the cost of stem cell transplant?
The cost of stem cell transplant can vary widely depending on factors such as the type of transplant, location, and healthcare provider, ranging from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Are there any risks or complications associated with stem cell transplant?
While stem cell transplant can be a life-saving procedure, it carries risks such as infection, graft-versus-host disease, organ damage, and potential long-term side effects. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to understand individual risks and benefits.
How long does the recovery process take after a stem cell transplant?
The recovery process varies for each patient, but it typically takes several months to a year for the immune system to fully recover, and ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are necessary.
Can anyone be a stem cell donor?
No, not everyone can be a stem cell donor. Donors need to undergo a thorough screening process to ensure compatibility and to assess their overall health. Specific eligibility criteria and guidelines are in place for potential donors.
What is the difference between autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplant?
Autologous stem cell transplant involves using the patient's own stem cells, while allogeneic transplant involves using stem cells from a donor. The choice between the two depends on the specific condition being treated and other individual factors, and it is determined by the healthcare team.
We are associated with experienced and highly skilled medical professionals. We use the latest medical technology available in the world and we provide medical services in collaboration with JCI & NABH Certified hospitals only. Our services include various types of treatment and organ restructuring and transplant.
