Spleen Removal (Splenectomy): Procedure, Reasons, and Recovery
Understanding the surgical removal of the spleen and its impact on health
Splenectomy, commonly referred to as spleen removal, is a surgical procedure performed to remove the spleen, an organ located in the upper left abdomen. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of splenectomy, including the procedure itself, reasons for undergoing splenectomy, the recovery process, and the potential complications associated with this surgery.
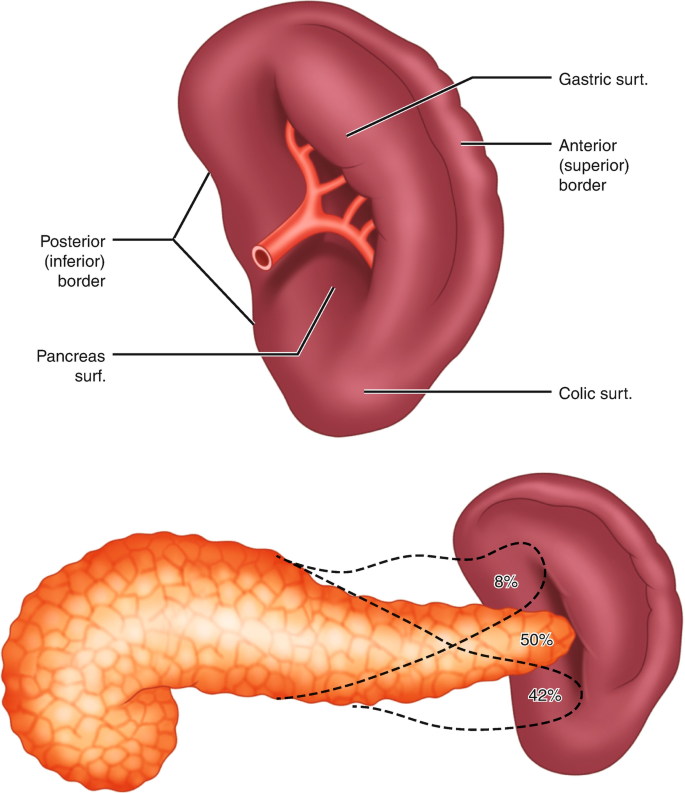
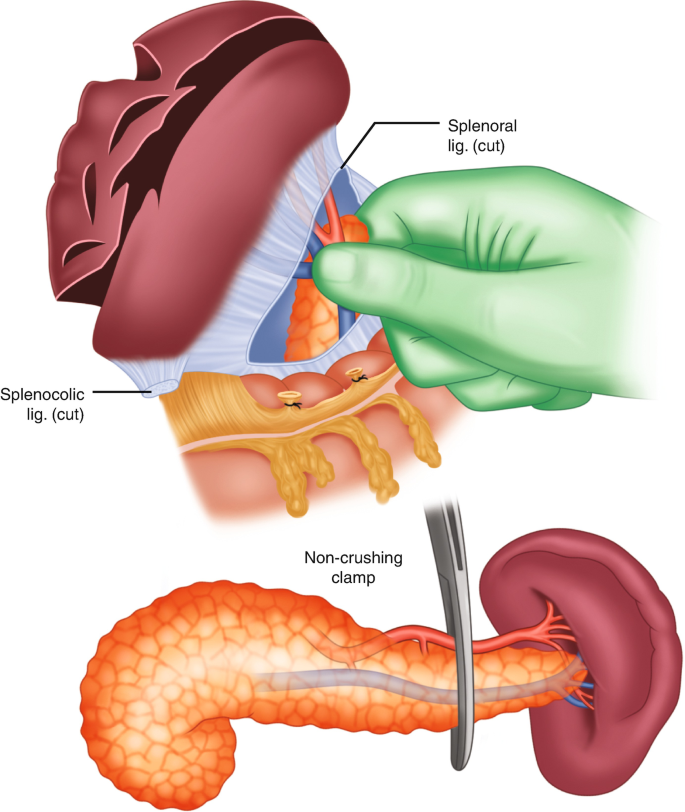 What is Splenectomy? Splenectomy is the surgical removal of the spleen, a vital organ responsible for filtering the blood, fighting infections, and producing and recycling red blood cells. The procedure can be performed using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, depending on the patient's condition and surgeon's preference.
What is Splenectomy? Splenectomy is the surgical removal of the spleen, a vital organ responsible for filtering the blood, fighting infections, and producing and recycling red blood cells. The procedure can be performed using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, depending on the patient's condition and surgeon's preference.
Reasons for Splenectomy: There are several medical conditions that may necessitate splenectomy, including:
The Splenectomy Procedure: Splenectomy can be performed through an open or laparoscopic approach. Open surgery involves making an incision in the abdomen to access and remove the spleen. Laparoscopic splenectomy, on the other hand, utilizes smaller incisions and specialized instruments to remove the spleen with minimal scarring and faster recovery.
Recovery and Living Without a Spleen: After splenectomy, patients will typically stay in the hospital for a few days for monitoring and pain management. Recovery time varies, but most individuals can resume normal activities within six to eight weeks. However, living without a spleen increases the risk of certain infections, particularly those caused by encapsulated bacteria. Vaccinations against these bacteria, such as pneumococcus, meningococcus, and Haemophilus influenzae type b, are usually recommended to reduce the risk of infections.
Potential Complications: While splenectomy is generally safe, there are potential risks and complications associated with the surgery. These may include postoperative infections, bleeding, blood clot formation, damage to surrounding organs, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. It is important to discuss these risks with the surgeon and follow the postoperative instructions carefully to minimize potential complications.
The success rate of splenectomy, or spleen removal, is generally high, with the procedure being successful in the majority of cases. However, the specific success rate may vary depending on the underlying condition being treated and the individual patient's health. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to assess the risks and benefits of splenectomy in each specific case.
Recovery time can vary, but most individuals can resume normal activities within six to eight weeks after the surgery.
Yes, but living without a spleen increases the risk of certain infections. Vaccinations and preventive measures are recommended to reduce this risk.
Complications may include postoperative infections, bleeding, blood clot formation, damage to surrounding organs, or adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Yes, vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria, such as pneumococcus, meningococcus, and Haemophilus influenzae type b, are typically recommended to prevent infections.
Yes, splenectomy can be performed using minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, which offer smaller incisions, faster recovery, and reduced scarring compared to open surgery.
It costs in India approximately 4000 USD in India.
We are associated with experienced and highly skilled medical professionals. We use the latest medical technology available in the world and we provide medical services in collaboration with JCI & NABH Certified hospitals only. Our services include various types of treatment and organ restructuring and transplant.
