Surgical Treatment Options for Oral Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview
A Comprehensive Overview of Surgical Approaches for Oral Cancer
Introduction:
Oral cancer is a serious condition characterized by the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the tissues of the oral cavity. It poses a significant health risk and can have detrimental effects on a person's quality of life. While several treatment modalities exist for oral cancer, surgery plays a crucial role in its management. This article provides an in-depth exploration of surgical treatment options for oral cancer, highlighting their benefits, risks, and outcomes.
Early Detection and Diagnosis:
Early detection of oral cancer is crucial for successful treatment outcomes. Regular dental check-ups, self-examinations, and awareness of the potential symptoms are vital in identifying the disease at its initial stages. If oral cancer is suspected, a biopsy is performed to confirm the diagnosis, enabling the healthcare team to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Surgical Treatment Options:
Tumor Excision:
Tumor excision involves surgically removing the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue surrounding it. This approach is commonly used for smaller tumors that haven't spread extensively. The primary goal is to eliminate the cancerous cells while preserving the function and aesthetics of the affected area.
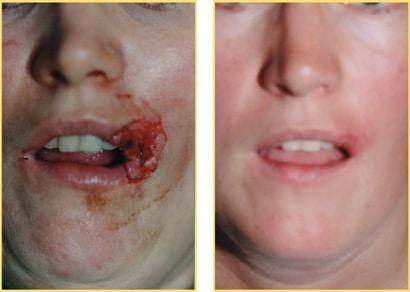
Mohs Surgery:
Mohs surgery, also known as microscopically controlled surgery, is employed for tumors located in areas where tissue preservation is critical, such as the lips or tongue. This precise technique involves the sequential removal and microscopic examination of thin layers of tissue until no cancer cells are detected, minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
Glossectomy or Mandibulectomy:
In advanced cases, when the tumor has spread extensively or invaded neighboring structures, partial or total glossectomy (removal of the tongue) or mandibulectomy (removal of the jawbone) may be necessary. These complex procedures require meticulous planning and often involve reconstructive surgery to restore function and appearance.
Benefits and Risks of Surgery:
Surgical treatment for oral cancer offers several benefits, including complete removal of the tumor, reduced risk of recurrence, and improved quality of life. However, surgery may entail potential risks such as bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding structures, and functional impairment. The healthcare team thoroughly evaluates each case to minimize risks and maximize the benefits of surgery.
Post-Surgical Care and Rehabilitation:
Following oral cancer surgery, proper post-operative care is crucial to ensure optimal healing and recovery. This may involve pain management, wound care, dietary modifications, and speech or swallowing therapy. Rehabilitation programs tailored to the patient's specific needs play a vital role in restoring oral function and enhancing overall well-being.
Conclusion:
Surgical treatment options play a significant role in the management of oral cancer, offering effective means to remove tumors and restore function. Early detection and diagnosis remain critical for successful outcomes. While surgery presents risks, careful planning, and post-operative care help minimize them. Through comprehensive evaluation, personalized treatment plans can be devised to optimize the benefits of surgery and improve the prognosis for individuals with oral cancer.
We are associated with experienced and highly skilled medical professionals. We use the latest medical technology available in the world and we provide medical services in collaboration with JCI & NABH Certified hospitals only. Our services include various types of treatment and organ restructuring and transplant.
