Myringoplasty: Restoring the Integrity of the Tympanic Membrane
Understanding the Surgical Procedure, Benefits, and Post-Operative Care
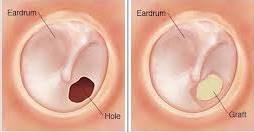
Introduction: Myringoplasty is a surgical procedure performed to repair perforations in the eardrum, scientifically known as the tympanic membrane. This delicate membrane separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear and plays a vital role in transmitting sound vibrations. When the eardrum sustains a perforation or hole, it can lead to hearing loss, recurrent ear infections, and other complications. Myringoplasty aims to restore the integrity of the tympanic membrane, improve hearing, and prevent further complications.
 The Significance of Myringoplasty: Myringoplasty is recommended when a perforation in the eardrum fails to heal spontaneously or persists for an extended period. The procedure helps to:
The Significance of Myringoplasty: Myringoplasty is recommended when a perforation in the eardrum fails to heal spontaneously or persists for an extended period. The procedure helps to:
Restore Hearing: A perforated eardrum often results in conductive hearing loss, where sound transmission is hindered. By repairing the perforation, myringoplasty can improve hearing ability.
Prevent Infections: A perforation in the eardrum increases the risk of recurrent ear infections. Myringoplasty closes the hole, reducing the likelihood of bacterial or fungal infections in the middle ear.
Protect the Middle Ear: The eardrum acts as a protective barrier for the middle ear. A repaired tympanic membrane safeguards the middle ear from debris, water, and foreign particles, minimizing the risk of complications.
The Myringoplasty Procedure: Before the surgery, a thorough examination and evaluation of the patient's ear condition are conducted. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves the following steps:
Incision and Flap Creation: An incision is made behind or inside the ear to access the eardrum. A small flap of tissue is then created near the perforation site to be used for grafting.
Graft Placement: The graft, usually obtained from the patient's own tissue (autograft) or an artificial material (tympanoplasty), is carefully placed over the perforation site. The graft is secured with specialized medical glue or small sutures.
Stabilization: To ensure proper healing and stability of the graft, a supporting material, such as a gel or a dissolvable packing material, may be used.
Eardrum Reinforcement: In some cases, additional procedures may be performed during myringoplasty to reinforce the eardrum, such as ossicular chain reconstruction or middle ear exploration.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery: Following myringoplasty, patients are typically advised to take the following precautions:
Avoid Water Entry: Patients should prevent water from entering the ear during the healing process. This may involve using earplugs or cotton balls coated with petroleum jelly during showers or swimming.
Medication and Ear Drops: Antibiotics and ear drops may be prescribed to prevent infection and aid in the healing process. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and usage instructions.
Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up visits with the otolaryngologist are essential to monitor the healing progress and address any concerns or complications.
Gradual Return to Normal Activities: Patients are usually advised to avoid strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting or blowing the nose forcefully, for several weeks after surgery. It's important to gradually reintroduce normal activities based on the doctor's guidance.
Conclusion: Myringoplasty is a valuable surgical intervention to repair perforations in the eardrum. By restoring the integrity of the tympanic membrane, this procedure can improve hearing, reduce the risk of infections, and protect the delicate structures of the middle ear. Understanding the myringoplasty process, benefits, and post-operative care guidelines enables patients to make informed decisions and promotes successful outcomes in restoring ear health.
Q&A
Q. What is myringoplasty?
A. Myringoplasty is a surgical procedure used to repair a perforated eardrum by grafting tissue onto the hole in order to restore its integrity and improve hearing.
Q. How long does it take to recover from myringoplasty?
A. Recovery time varies, but most patients can expect to experience temporary ear discomfort and hearing loss for a few weeks after the procedure, with a full recovery typically taking several months.
Q. What are the risks associated with myringoplasty?
A. Although rare, potential risks include infection, bleeding, scarring, dizziness, and persistent hearing loss. It's important to discuss these risks with your doctor before undergoing the surgery.
Q. Can myringoplasty completely restore hearing?
A. While myringoplasty aims to improve hearing, the extent of improvement varies from person to person. Factors such as the size and location of the perforation, the condition of the middle ear, and individual healing abilities can impact the outcome.
Q. Is myringoplasty performed under general anesthesia?
A. Myringoplasty can be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation, depending on the preference of the patient and the surgeon. The choice of anesthesia will be discussed during the pre-operative consultation.
We are associated with experienced and highly skilled medical professionals. We use the latest medical technology available in the world and we provide medical services in collaboration with JCI & NABH Certified hospitals only. Our services include various types of treatment and organ restructuring and transplant.
