Understanding Meningioma: Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction to Meningioma
Meningioma is a type of tumor that arises from the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. These tumors typically grow slowly and are often benign, but in some cases, they can be malignant or aggressive. Meningiomas are the most common primary brain tumors, accounting for approximately 30% of all brain tumors.
Types of Meningioma
There are several different types of meningiomas, classified based on their location and histopathological characteristics. The most common types include:
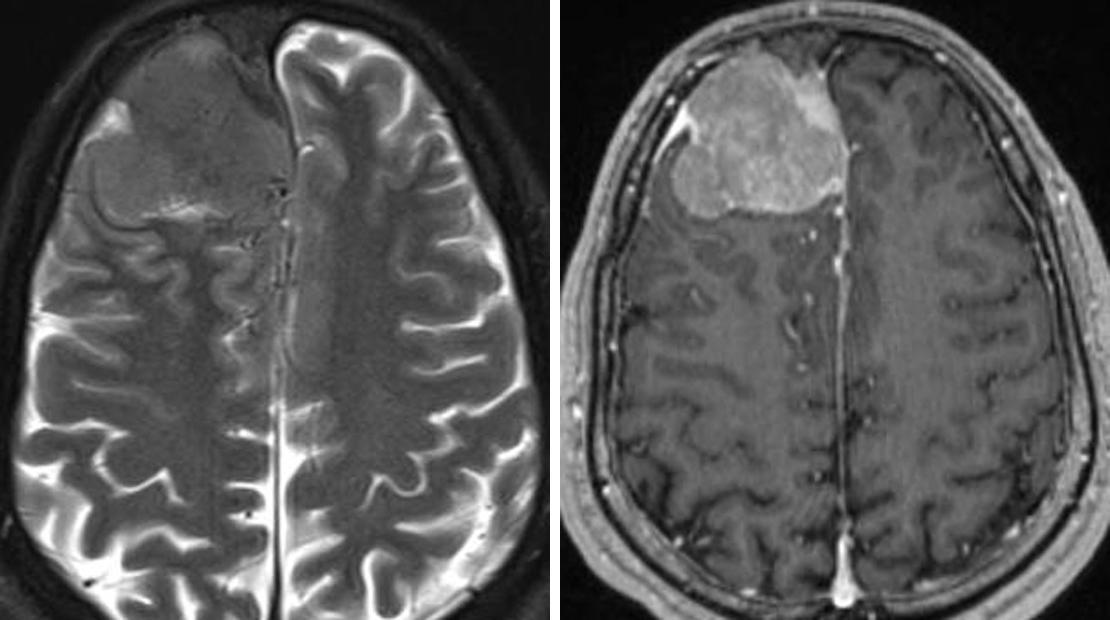
Convexity Meningiomas: These tumors occur on the outer surface of the brain, primarily on the convexities or the top of the cerebral hemispheres.
Skull Base Meningiomas: These tumors are located at the base of the skull and can affect various regions, such as the sphenoid wing, olfactory groove, and posterior fossa.
Parasagittal and Falx Meningiomas: These tumors develop along the midline, typically attached to the sagittal sinus or falx cerebri.
Sphenoid Wing Meningiomas: These tumors originate from the sphenoid wing, which is a bony structure on the side of the skull.
Symptoms and SignsThe symptoms of meningioma can vary depending on the tumor's location, size, and proximity to vital structures. Common signs and symptoms may include:
Diagnosis
To diagnose meningioma, a healthcare professional will consider the patient's medical history, perform a physical examination, and recommend further tests, such as:
Imaging Tests: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans provide detailed images of the brain, helping identify the presence, location, and size of the tumor.
Biopsy: In some cases, a small tissue sample may be obtained through a surgical procedure to determine if the tumor is benign or malignant.
Treatment Options:
The appropriate treatment for meningioma depends on various factors, including the tumor's size, location, and grade. Treatment options may include:
Observation: If the meningioma is small, asymptomatic, and not causing any complications, a "watch and wait" approach may be recommended with regular monitoring.
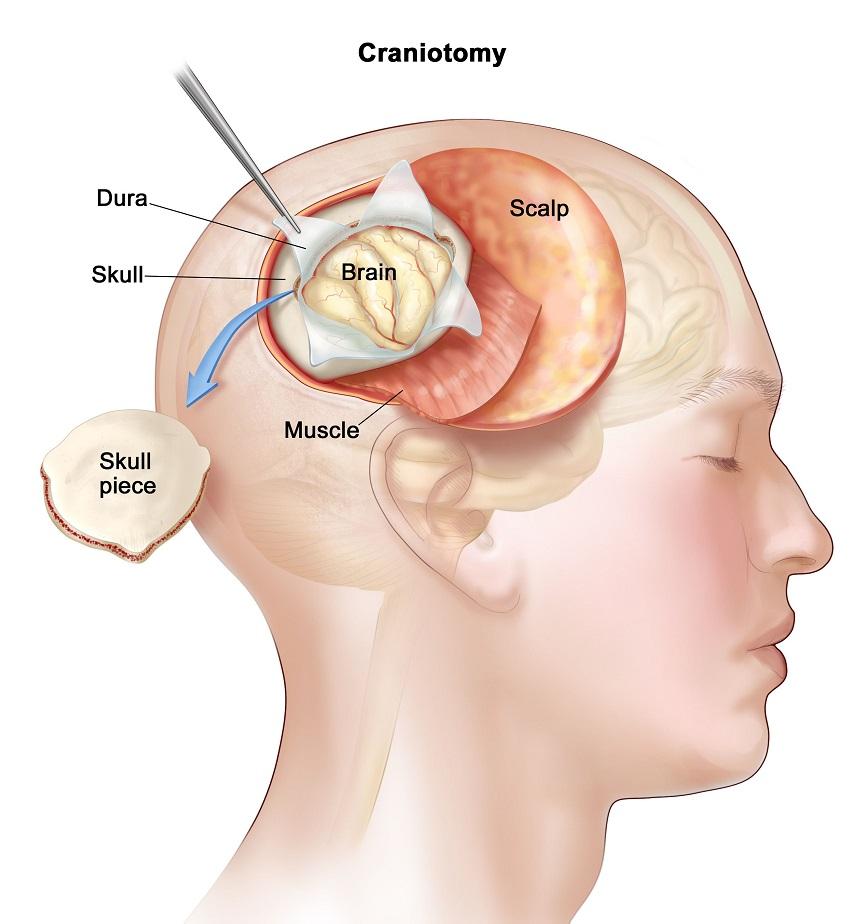
Surgery: Surgical removal is often the primary treatment for meningiomas. The goal is to remove the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy brain tissue.
Radiation Therapy: In cases where complete removal is not possible or if the tumor recurs, radiation therapy may be utilized to destroy remaining tumor cells.
Medications: Some meningiomas may be treated with targeted therapies or medications that can slow tumor growth or help manage symptoms.
Conclusion
Meningioma is a prevalent type of brain tumor that originates from the meninges. While often benign, meningiomas can present various symptoms depending on their location. Accurate diagnosis through imaging and, if necessary, a biopsy, is essential for determining the appropriate treatment strategy. Treatment options include observation, surgical removal, radiation therapy, and medication, depending on the tumor characteristics and individual patient factors. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are crucial for long-term management and improved outcomes for individuals with meningioma.
We are associated with experienced and highly skilled medical professionals. We use the latest medical technology available in the world and we provide medical services in collaboration with JCI & NABH Certified hospitals only. Our services include various types of treatment and organ restructuring and transplant.
