Comprehensive Treatment for Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction (CIP)
Understanding Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction (CIP)
Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction (CIP) is a rare gastrointestinal disorder characterized by impaired movement of the intestines, leading to symptoms similar to a mechanical obstruction. It affects the normal muscular contractions that propel food and waste through the digestive system. CIP can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon. This condition can cause chronic symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and constipation or diarrhea.
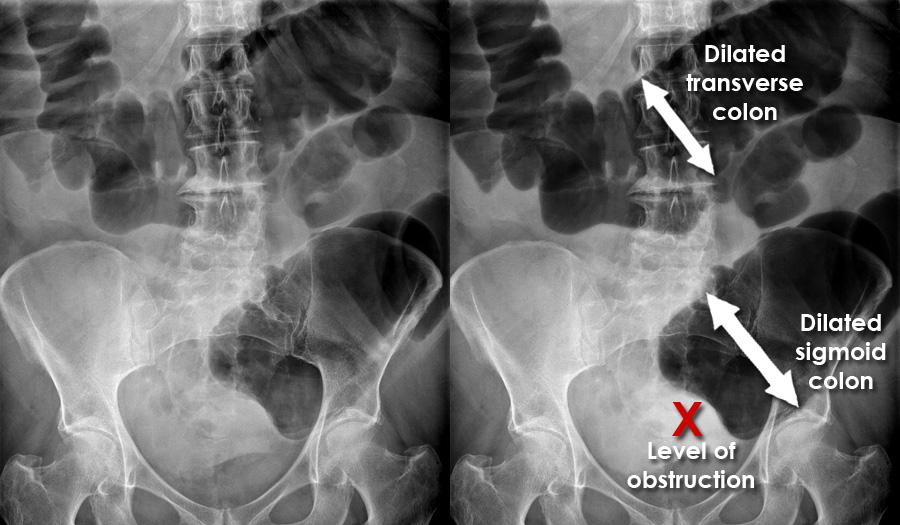
Treatment Options for Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction (CIP)
Managing Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction (CIP) involves a comprehensive approach aimed at improving intestinal motility and alleviating symptoms. The treatment plan may vary depending on the severity of the condition, individual symptoms, and underlying causes. Here are some of the commonly used treatment options for CIP:
Medications: Medications are often prescribed to manage symptoms associated with CIP. Prokinetic drugs such as metoclopramide and erythromycin may be used to stimulate intestinal contractions and improve motility. Other medications like antiemetics and laxatives may also be prescribed to relieve specific symptoms.
Dietary Modifications: Dietary changes play a crucial role in managing CIP. A registered dietitian can help develop a personalized meal plan that focuses on easily digestible foods, adequate hydration, and balanced nutrition. In some cases, a feeding tube or parenteral nutrition (intravenous feeding) might be necessary if oral intake is insufficient.
Nutritional Support: In severe cases of CIP where oral intake is inadequate or ineffective, nutritional support becomes essential. Enteral nutrition, delivered through a feeding tube directly into the digestive tract, can provide necessary nutrients. In more extreme cases, parenteral nutrition may be required, delivering nutrients intravenously.
Surgical Interventions: Surgery is typically considered when other treatment options fail to provide relief. Surgical procedures may aim to remove obstructions, repair damaged portions of the intestines, or create alternative pathways for digestion. However, surgery is reserved for specific cases and requires careful consideration.
Symptom Management: Various methods are employed to manage specific symptoms of CIP. For instance, antispasmodic drugs may be prescribed to relieve abdominal pain and cramping. Additionally, laxatives, enemas, or manual decompression techniques may be utilized to alleviate constipation or manage bowel movements.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy techniques can help improve intestinal motility and alleviate symptoms. Modalities such as abdominal massage, exercises, and relaxation techniques may be incorporated into the treatment plan to stimulate bowel activity.
Conclusion
Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction (CIP) is a complex condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. By combining medications, dietary modifications, nutritional support, surgical interventions (in select cases), symptom management, and physical therapy, healthcare professionals can help patients with CIP manage their symptoms, improve intestinal motility, and enhance their quality of life. If you suspect you may have CIP or are experiencing persistent gastrointestinal symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
We are associated with experienced and highly skilled medical professionals. We use the latest medical technology available in the world and we provide medical services in collaboration with JCI & NABH Certified hospitals only. Our services include various types of treatment and organ restructuring and transplant.
