Correcting Congenital Heart Defects with the Arterial Switch Operation
Introduction:
The arterial switch operation is a complex surgical procedure used to correct certain congenital heart defects. In this blog, we will delve into the details of this procedure, including its benefits, the surgical process itself, and what to expect during the recovery period. Understanding the arterial switch operation can provide valuable insights into the treatment options available for individuals with specific heart conditions.
 What is the Arterial Switch Operation?
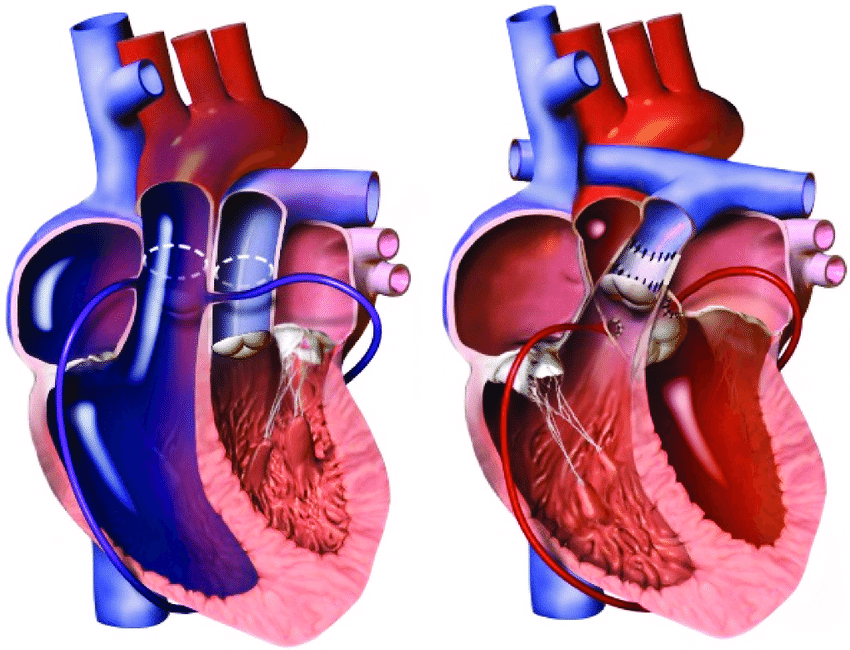
What is the Arterial Switch Operation?
The arterial switch operation is a surgical procedure performed to correct transposition of the great arteries (TGA), a congenital heart defect where the pulmonary artery and aorta are switched in their positions.
This procedure involves reconnecting the coronary arteries to the newly positioned aorta and rerouting the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle.
Benefits of the Arterial Switch Operation:
The Arterial Switch Operation Procedure:
Preoperative Evaluation:
Prior to the surgery, a comprehensive evaluation is conducted, including imaging tests, cardiac catheterization, and assessments of overall health.
Anesthesia and Incision:
General anesthesia is administered, and an incision is made in the chest to access the heart and major blood vessels.
Cardiopulmonary Bypass:
The patient is connected to a heart-lung bypass machine, which temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during the procedure.
Arterial Switch and Coronary Artery Repositioning:
The pulmonary artery and aorta are disconnected, and the coronary arteries are carefully reattached to the new aortic position.
The pulmonary artery is then connected to the right ventricle.
Recovery after the Arterial Switch Operation:
Conclusion: The arterial switch operation is a specialized surgical procedure designed to correct specific congenital heart defects.
By understanding the benefits, procedure, and recovery process associated with this operation, individuals and their families can make informed decisions and have confidence in the potential for improved cardiac health and quality of life.
Arterial aneurysms can be caused by various factors, including atherosclerosis, genetic predisposition, trauma, infection, or inflammation. High blood pressure is a significant contributor to the development and progression of arterial aneurysms.
In many cases, arterial aneurysms do not cause symptoms until they rupture. However, some individuals may experience localized pain, pulsating sensations, or other symptoms depending on the location of the aneurysm.
Not all arterial aneurysms require surgery. Small and stable aneurysms may be managed through monitoring and lifestyle changes. The decision for surgery depends on factors such as the size, location, and overall health of the patient.
The recovery time varies based on the type of treatment. Minimally invasive procedures often have shorter recovery periods compared to open surgery. Post-treatment care includes follow-up appointments and lifestyle modifications.
The risk of rupture depends on various factors, including the size and location of the aneurysm. Larger aneurysms and those located in critical arteries pose a higher risk of rupture, which can lead to life-threatening complications.
We are associated with experienced and highly skilled medical professionals. We use the latest medical technology available in the world and we provide medical services in collaboration with JCI & NABH Certified hospitals only. Our services include various types of treatment and organ restructuring and transplant.
